Sales Forecasting (Time-Series)
Predict weekly sales across products & locations using classical + ML models; enable inventory and promo planning.
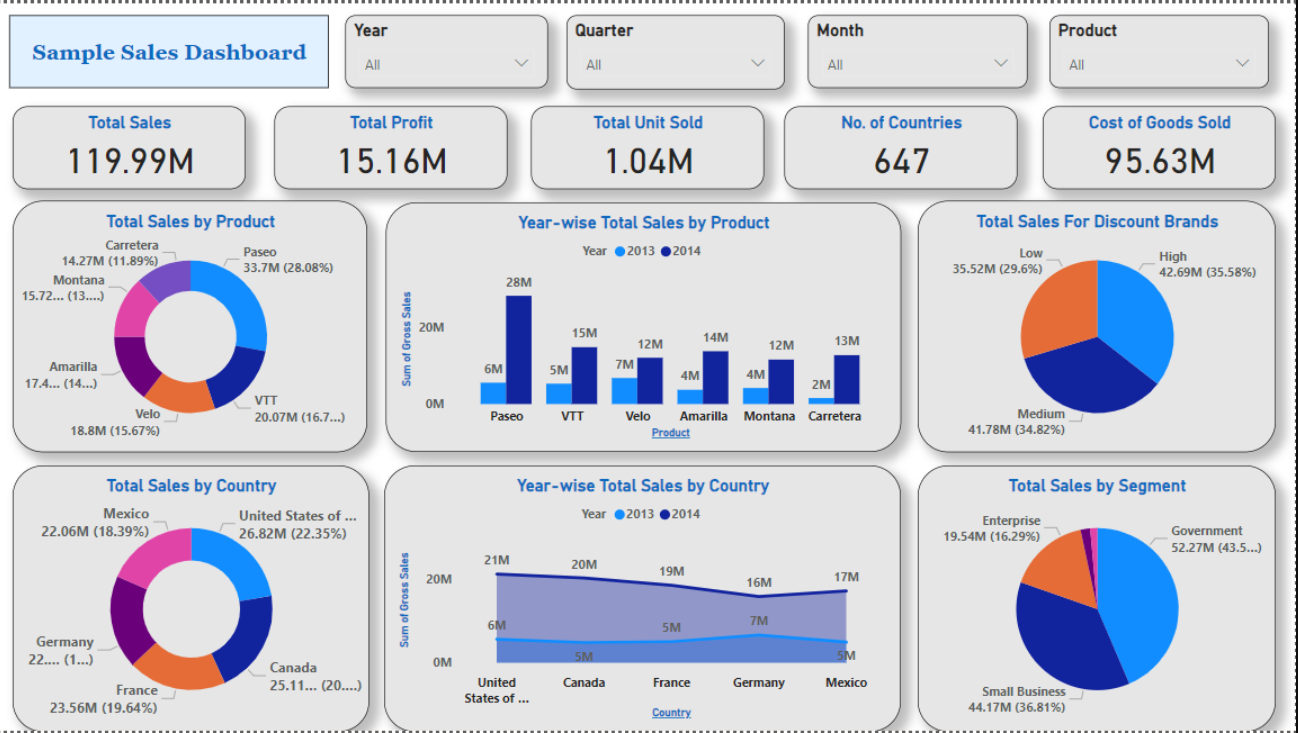
Overview
We built a forecasting pipeline that learns seasonality, promotions, holidays, and price elasticity to predict weekly sales per product–location. A Power BI dashboard visualizes forecasts, uncertainty, and bias, helping planners align inventory and campaigns.
Time-Series CV
Lag/Window Features
Hierarchical Aggregation
Deployment to BI
Data
- Grain: weekly product × store (3–5 years history)
- Signals: calendar, holidays, promos, prices, weather, stockouts
- Targets: units and/or revenue; forecast horizon typically 8–12 weeks
Approach
- Baselines: Naïve, seasonal naïve, ETS.
- Classical: SARIMA / Prophet for strong weekly/annual seasonality.
- ML: Gradient boosting (XGBoost) with lags, rolling means, promo/price features.
- Validation: Rolling-origin time-series CV; metrics: MAPE/WAPE/sMAPE/RMSE.
- Ensemble: Blend classical + ML per series based on validation rank.
# sketch: lag/window features for ML
def add_lag_feats(df, lags=(1,2,3,4,5,6,7,14,28), windows=(7,28)):
for L in lags:
df[f"y_lag_{L}"] = df.groupby(["store","sku"])["y"].shift(L)
for W in windows:
df[f"y_ma_{W}"] = (df.groupby(["store","sku"])["y"]
.shift(1).rolling(W, min_periods=1).mean())
return df
# sketch: rolling-origin cross-validation
def rolling_cv(df, n_folds=4, horizon=8):
folds = []
end = df["ds"].max()
for k in range(n_folds):
cutoff = end - pd.Timedelta(weeks=(n_folds-k)*horizon)
tr = df[df["ds"] <= cutoff]
va = df[(df["ds"] > cutoff) & (df["ds"] <= cutoff + pd.Timedelta(weeks=horizon))]
folds.append((tr, va))
return folds
↓ 27%
MAPE vs baseline
↓ 18%
WAPE vs last season
± 9.3%
Avg. forecast band
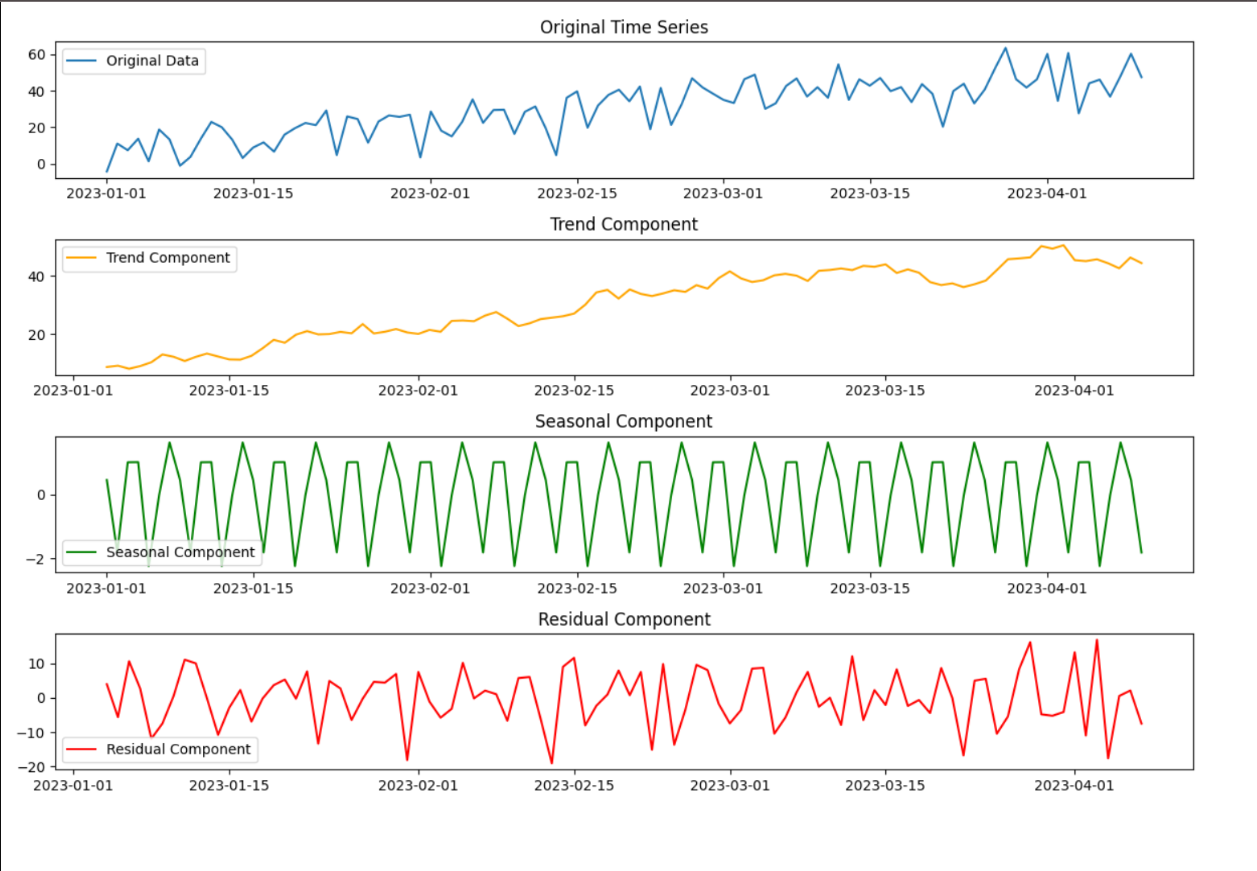
Architecture (simplified)
Jobs scheduled; forecasts published to BI with versioned artifacts.
Tech Stack
Python · Pandas · Prophet / SARIMA · XGBoost · scikit-learn · Power BI · (optional) Power Automate